
![]()
To compare the performance of the DEAR scheme with that of application-controlled file caching (ACFC) [12], we performed trace-driven simulations with the same set of three application traces used in [12]. The characteristics of the three applications and their traces can be found in [12]. Figure 10 shows the miss ratio of the three applications for the LRU, ACFC, DEAR, and OPT (off-line optimal) schemes when cache size increases from 1MB to 16MB. The results for the LRU, ACFC, and OPT schemes were borrowed from [12] and those for the DEAR scheme were obtained by simulating the DEAR scheme with detection period equal to 500 and the number of sublists in the ordered list equal to 5 for both backward distance and frequency block attribute types. The results show that the miss ratio of the DEAR scheme is comparable to that of the ACFC scheme, which utilizes user-level hints to guide the replacement decisions. The small difference between the two schemes results from the misses that occur before the DEAR scheme has a chance to detect the reference pattern.
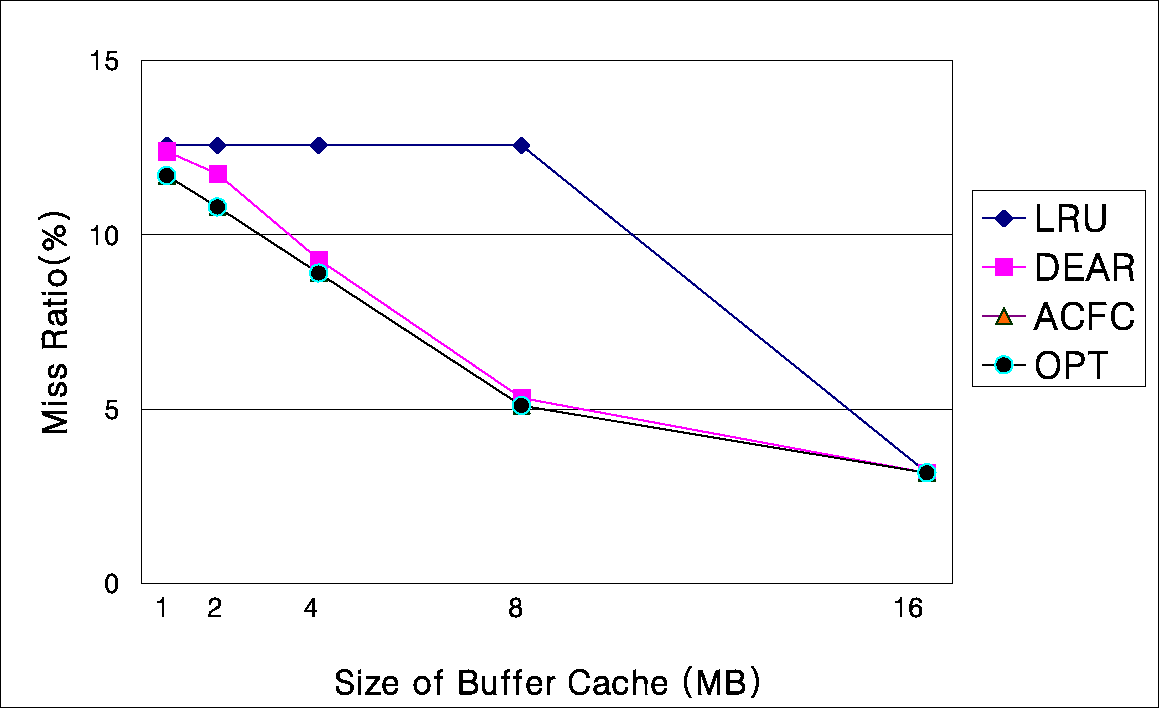 (a) cscope
(b) linking kernel
(c) Postgres |
Figure 10: Comparison with application-controlled file caching.
![]()