


Next: Synchronization
Up: System Architecture
Previous: System Architecture
In this subsection we describe the basic operations in the prefetch
thread and its interaction with the computation thread
and the prefetch library.
Figure 2:
Computation thread (left) and prefetch thread (right). The main
function without the lines marked by ## is the original
application code. This code is modified to add a prefetch thread
represented by the prefetch function. The lines in the prefetch
function that are not marked with $$ are extracted from the
original main function. Other additional functions are added for the
two threads to communicate with each other. Notice that the
computation part of the main function does not appear in the
prefetch function
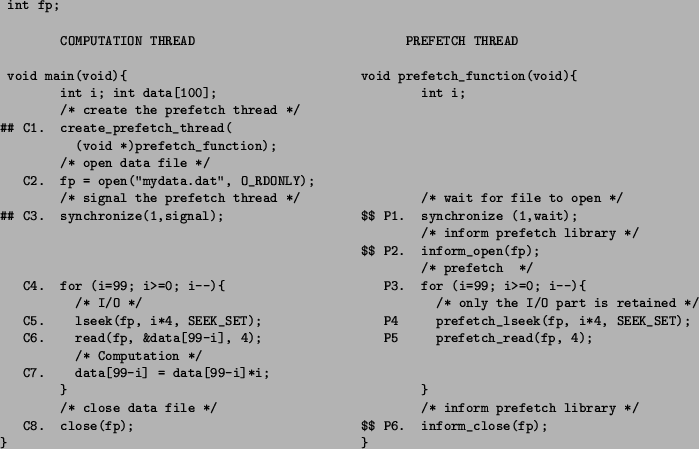 |
Figure 2 shows how AASFP's translator converts an example application
into a computation and a prefetch
thread. The programming interface provided by the prefetch library
includes the following four calls:
- create_prefetch_thread (prefetch_function):
This function allows an application to fork a prefetch
thread, and to execute the
prefetch_function.
The prefetch_function is passed as the input argument,
as shown in line 1 of Figure 2.
- prefetch_XXX():
These are a set of functions that the prefetch
thread can use to specify prefetch calls. The
prefetch calls replace the original I/O calls and use
almost the same syntax. For example, for the I/O
call read(stream, ptr, size), AASFP provides the
prefetch call prefetch_read(stream, size). The
parameter ptr for the data is not needed, since
the prefetch call only generates the target data's starting address but never
actually performs the real I/O. Lines P4 and P5 in Figure 2 represent the prefetch
calls corresponding to the I/O calls at lines C5 and C6 of
the main function respectively.
- inform_open(file_pointer), inform_close(file_pointer):
These two functions are used by the prefetch thread to inform
the prefetch library that some file is opened
or closed. Such notification is necessary so that the prefetch library can maintain
a file table consisting of {file pointer, current offset}
for those files accessed by the prefetch thread. Lines P2 and P6 in Figure 2
represent the inform calls corresponding to the open and close
system calls in the computation thread.
- synchronize(synchronization_point, type):
This function synchronizes the two threads. The argument
type can be signal or wait. Synchronization
is discussed in detail in the next subsection.


Next: Synchronization
Up: System Architecture
Previous: System Architecture
chuan-kai yang
2002-04-15


