 |

This category includes functions that modify controlled objects
without any security checks. The code segment in
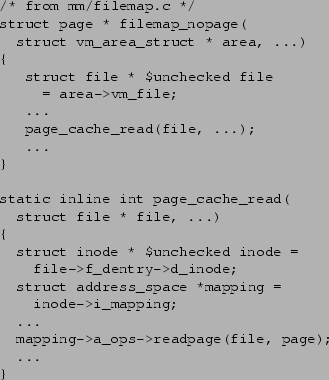
Figure 10 shows an example of such cases. The function
filemap_nopage() is called when a page fault occurs within an
m'mapped region. Since there is no check on the file object
within the function, its type is
unchecked. It is then passed to function
page_cache_read(), which in turn calls
mapping->a_ops->readpage(), which expects a checked file
object. This code path shows that once a file is mapped into a
process address space, the process can access the file even after
security attributes of the file have changed.
Since there is an LSM authorization hook to verify read access to a
file on each read call, this is inconsistent with the current
hooks. A discussion with the LSM community revealed that enforcement
on each read is optional and will only be used for files that
are not m'mapped. This hooks, as well as the one for checking access
on write have been documented to clarify this inconsistency.
In other cases, for example function iput(), it seems that
checks are not necessary, as the
function is used for reference counting. In other cases, such as
initialization function clean_inode() for the inode
data structure, there is no need for security protection, as
modification of the data structure
is restricted to zeroing and initialization of the contents. We call
these functions ``safe'' functions and consider type errors induced by
these functions as false positives.