![[*]](foot_motif.gif)

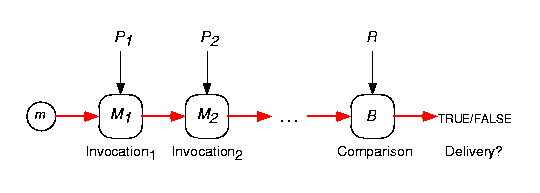
A condition C=(A, R, B) represents a single
condition that a message object m must fulfill in order to be
delivered. B is a comparison function which can be viewed as a
binary predicate: B(o1: obj, o2: obj): bool.
The two arguments are (1) a predefined result R and (2) the result of the
invocation chain represented by the accessor A. A condition is thus
evaluated against a message object m, and evaluates positively iff
m satisfies that condition: C(o: obj): bool, and C(m) = B(R, A(m)).
Figure 6 outlines the different evaluation stages of a condition.
A similar scheme can be found for object queries in object-oriented data
management systems, e.g., TIGUKAT [SO95].![[*]](foot_motif.gif)