



Next: Implementation of HLRC on
Up: Protocol Design
Previous: Asynchronous Entry Point
Figure 1:
Coherence Messages exchanged by three processes in HLRC
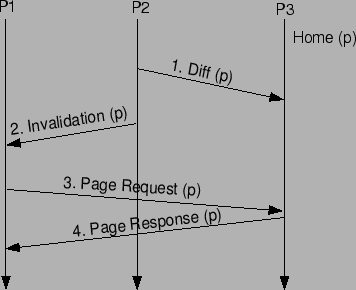 |
The protocol activity generates two types of messages:
coherence messages and
synchronization messages.
The coherence messages are related
to update propagation and fall in one of the following categories:
- Diffs - sent by a writer of the page to the home of the page
at release or acquire time; contain the updates
performed by the sender since the last release or acquire.
- Invalidations - sent at acquire time by the last releaser;
contain a list of pages that were updated at the
last releaser and elsewhere, that the acquirer must update.
- Page fetch request - sent at page fault time to the home.
- Page response - sent by the home to the faulting node as a response
to the page fetch request message.
Table 1:
Application characteristics
| Applications |
Problem Size |
Sequential Time (s) |
Shared memory size |
| Barnes-Spatial |
262144 bodies |
357 |
325 MB |
| FFT |
2048x2048 |
86 |
196 MB |
| LU |
2048 x 2048 |
209 |
33 MB |
| Ocean |
514 x 514 |
30 |
97 MB |
| Radix |
45M keys |
95 |
377 MB |
| Water-Nsquared |
32768 molecules, 5 steps |
22450 |
22 MB |
| Water-Spatial |
262144 molecules |
14202 |
264 MB |
|
Figure 1 illustrates the flow of coherence
messages when a shared page (p) is updated by a process (P2) and subsequently
accessed by another process (P1).
The timing and order of the coherence operations are determined by
the consistency model implemented by the DSM system. For example, in
homeless LRC, the diff messages are sent lazily on demand,
while in the home-based LRC, diffs are sent eagerly, either at
release or acquire time.
The synchronization messages are used to implement the distributed
queue for locks and the distributed barrier. In most software
DSM protocols, especially in LRC, coherence messages and synchronization
messages are combined in a single message whenever possible. For
example, in LRC, the invalidation message is combined with the reply
message to a lock acquire.



Next: Implementation of HLRC on
Up: Protocol Design
Previous: Asynchronous Entry Point
Murali Rangarajan
2000-08-09

