


Next: Analysis of WM Technique
Up: Implementation of WM system
Previous: Merging multiple sniffers
Sniffer placement
We used SNR measurements to place our multiple sniffers. One
sniffer was placed adjacent to the AP, to be responsible for capturing the
From-AP traffic and the traffic of clients near the AP. The other
sniffers were placed as close as possible to the wireless
clients. Assuming that clients are uniformly
distributed over the coverage area, this meant placing the
sniffers so that they cover as much of the AP's coverage area as
possible. Generally, if we have 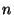 sniffers to place, we
split the AP coverage area into
sniffers to place, we
split the AP coverage area into 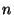 equal areas and place the
sniffers in the center of mass of these areas.
equal areas and place the
sniffers in the center of mass of these areas.
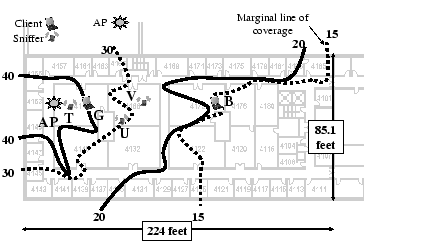
Figure 1:
SNR Contour Map for controlled experiment: SNR Contour lines for
40, 30, 20 and 15 dB were obtained from SNR measurements. We
placed the wireless clients at the locations with different signal
conditions based on SNR measurement. Sniffers were placed at
locations T, U and V.
 |
To determine the AP coverage area, we first used the SNR (obtained
from Prism2 header) seen in Beacon frames from the target AP
to draw the contour lines
(as shown in Figure 1). The AP coverage area was
then determined by choosing a particular SNR contour, e.g., the
15-dB contour line.
We can refine this strategy by noting that, in an environment
where multiple APs are installed, the coverage area of an AP may
be reduced to the Association Area of the AP. The
Association Area of an AP is the area at which a client
will favor this AP for association compared with other APs in the
area. This behavior may be device-specific and may also
vary depending on whether a client has roamed to an area or has
just powered on their radio. For the purposes of sniffer
placement, we assume that clients will associate with the AP with
the highest SNR 9 (9).


Next: Analysis of WM Technique
Up: Implementation of WM system
Previous: Merging multiple sniffers
Jihwang Yeo
2005-05-10


