Next: Enterprise Workloads Up: Experimental Evaluation Previous: End-to-End Control

Earlier we showed that PARDA maintains high utilization of the array
even when some hosts idle, by allowing other hosts to increase their
window sizes. However, if one or more VMs become idle, the
overall ![]() of the host must be adjusted, so that backlogged VMs
on the same host don't obtain an unfair share of the current capacity.
Our implementation employs the
technique described
in Section 3.4.
of the host must be adjusted, so that backlogged VMs
on the same host don't obtain an unfair share of the current capacity.
Our implementation employs the
technique described
in Section 3.4.
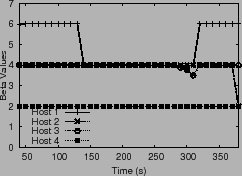
We experimented with dynamically idling one of the OLTP VM workloads
running on host 1 from the previous experiment presented in
Figure 12. The VM workload is stopped at ![]() = 140 s and
resumed at
= 140 s and
resumed at ![]() = 310 s. Figure 13 shows that the
= 310 s. Figure 13 shows that the ![]() value for host 1 adapts quickly to the change in the VM
workload. Figure 12(a) shows that the window size begins to
decrease according to the modified lower value of
value for host 1 adapts quickly to the change in the VM
workload. Figure 12(a) shows that the window size begins to
decrease according to the modified lower value of ![]() starting
from
starting
from ![]() = 140 s. By
= 140 s. By ![]() = 300 s, window sizes have converged to a
= 300 s, window sizes have converged to a ![]() ratio, in line with aggregate host shares. As the OLTP workload
becomes active again, the dynamic increase in the
ratio, in line with aggregate host shares. As the OLTP workload
becomes active again, the dynamic increase in the ![]() of host 1
causes its window size to grow.
This demonstrates that PARDA ensures fairness even in the presence of
non-backlogged workloads, a highly-desirable property for
shared storage access.
of host 1
causes its window size to grow.
This demonstrates that PARDA ensures fairness even in the presence of
non-backlogged workloads, a highly-desirable property for
shared storage access.
 |
Ajay Gulati 2009-01-14