 Storage capacity can change dramatically due to workload changes or
array accesses by uncontrolled hosts external to PARDA. We have
already demonstrated in Section 5.3.2 that
our approach is able to absorb any spare capacity that becomes
available. To test the ability of the control algorithm to handle
decreases in capacity, we conducted an experiment starting with the
first five hosts from the previous experiment. At time
Storage capacity can change dramatically due to workload changes or
array accesses by uncontrolled hosts external to PARDA. We have
already demonstrated in Section 5.3.2 that
our approach is able to absorb any spare capacity that becomes
available. To test the ability of the control algorithm to handle
decreases in capacity, we conducted an experiment starting with the
first five hosts from the previous experiment. At time 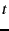 = 230 s, we
introduce a sixth host that is not under PARDA control. This
uncontrolled host runs a Windows Server 2003 VM issuing 16 KB random
reads to a 16 GB virtual disk located on the same LUN as the others.
= 230 s, we
introduce a sixth host that is not under PARDA control. This
uncontrolled host runs a Windows Server 2003 VM issuing 16 KB random
reads to a 16 GB virtual disk located on the same LUN as the others.
With 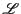 = 30 ms and a share ratio of
= 30 ms and a share ratio of 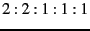 for the
PARDA-managed hosts, Figure 11 plots the usual metrics
over time. At
for the
PARDA-managed hosts, Figure 11 plots the usual metrics
over time. At 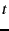 = 230 s, the uncontrolled external host starts, thereby
reducing available capacity for the five controlled hosts. The
results indicate that as capacity changes, the hosts under control
adjust their window sizes in proportion to their shares, and observe
latencies close to
= 230 s, the uncontrolled external host starts, thereby
reducing available capacity for the five controlled hosts. The
results indicate that as capacity changes, the hosts under control
adjust their window sizes in proportion to their shares, and observe
latencies close to 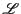 .
.
Figure 11:
Capacity Fluctuation. Uncontrolled external host added
at 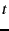 = 230 s. PARDA-controlled hosts converge to
new window sizes.
= 230 s. PARDA-controlled hosts converge to
new window sizes.
|
|
|
| (a) Window Size |
(b) Latency (ms) |
(c) Throughput (IOPS) |
|
Ajay Gulati
2009-01-14

![]() = 30 ms and a share ratio of
= 30 ms and a share ratio of ![]() for the
PARDA-managed hosts, Figure 11 plots the usual metrics
over time. At
for the
PARDA-managed hosts, Figure 11 plots the usual metrics
over time. At ![]() = 230 s, the uncontrolled external host starts, thereby
reducing available capacity for the five controlled hosts. The
results indicate that as capacity changes, the hosts under control
adjust their window sizes in proportion to their shares, and observe
latencies close to
= 230 s, the uncontrolled external host starts, thereby
reducing available capacity for the five controlled hosts. The
results indicate that as capacity changes, the hosts under control
adjust their window sizes in proportion to their shares, and observe
latencies close to ![]() .
.