



Next: Description of the Advanced
Up: Applications
Previous: Secure Storage ICs
The modular arithmetic coprocessor must have at least 6 registers (4 if only encryption is implemented),
each of length greater or equal than 16 bytes each. On the other hand, the coprocessor
shall be able to perform the following arithmetic and logical operations:
- Multiplication in
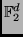 ,
,
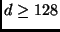 , of a long register by an 8-bit value,
, of a long register by an 8-bit value,
- Addition modulo 2 (
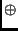 , i.e. exclusive OR) of two long registers,
, i.e. exclusive OR) of two long registers,
- Right and Left shifting of a long register,
- Logical AND of two long registers (optional),
- Simultaneous rotation of 4 bytes words (optional).
The following figure gives an example how such a coprocessor could look like:
Figure 1:
Example of the copprocessor's architecture.
|
|
Here, it is supposed that the standard CPU can directly operate on the data stored on the coprocessorīs
registers but that operations on these registers are much less efficient than on the standard CPU internal
registers, because the data stored in those registers have to be transferred to the CPU through some external bus,
as these data are usually organized as a so called XRAM.



Next: Description of the Advanced
Up: Applications
Previous: Secure Storage ICs
Roger Fischlin
2002-09-25
