



Next: Load distribution of different
Up: User Behavior Analysis
Previous: User Behavior Analysis
Spatial Locality
Spatial locality of user interest is about determining whether people in the
same geographical region tend to receive similar notification content. To
carry out our analysis we take the following approach. We define a
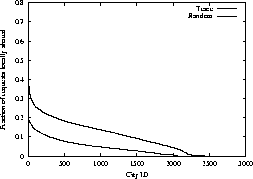
notification message to be locally shared if at least two users in the same
cluster receive the notification. We compare the degree of sharing using
geographical clustering and four random clusterings. In the geographical
clustering case, clients in the same city are clustered together. In the
random clustering case, clients are clustered randomly with the cluster size
being the same as in geographical clustering. We obtained the geographical
location of users using a registration database which contains zip code
information for each user. The zip code information is not clean -- some
users supplied invalid zip codes; we filter out all the zip codes that are not
5 digits. 14% of the users supplied such invalid zip codes. In the remaining
entries, it is still possible to have zip codes that do not match the actual
user location, but the fraction is likely to be small. Furthermore, when
computing the degree of local sharing, we exclude the cities to which fewer
than 100 notification messages were sent over the course of the week.
As shown in Figure 7, clients residing in the same city
have significantly more sharing in notification content compared to the
clients picked at random. We also compared geographical clustering with three
other random clusterings and observed similar results. The higher degree of
sharing in notification messages for clients in the same geographical region
indicates that localized services are popular for notification services. For
example, people living in New York are interested in receiving notification
messages about weather or events in New York. The geographical locality in
notification content implies that placing servers (i.e., either notification
server replicas or servers in an overlay network that provide
application-level multicast) close to popular geographical clusters can be
useful in reducing network load.
Figure 7:
Compare the local sharing between random clients and clients that are geographically close together.
 |



Next: Load distribution of different
Up: User Behavior Analysis
Previous: User Behavior Analysis
Lili Qiu
2002-04-17


