


Next: Implementations
Up: The Design and Implementation
Previous: The Kerberized Key Management
TCFS does not employ a fixed encryption scheme but
for each file a different encryption engine can be specified.
Encryption engines need to conform to a specific interface
and, in the Linux implementation, can be kernel loadable
module. Modules for all the major encryption scheme are
provided with the implementations.
Having modular encryption,
allows user to plug into TCFS its own encryption module for
increased user security.
Modular encryption allows users and system administrator to pick
their favorite block encryption scheme. Thus, for this section we denote by
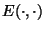 and
and
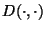 the encryption and
decryption algorithm associated with the encryption scheme
actually employed (see Figure 3).
The size of the block encrypted by the
encryption need not to be equal to the block size of the file.
Each file has a header that contains some information about the
file itself (e.g., TCFS version number, cipher id).
the encryption and
decryption algorithm associated with the encryption scheme
actually employed (see Figure 3).
The size of the block encrypted by the
encryption need not to be equal to the block size of the file.
Each file has a header that contains some information about the
file itself (e.g., TCFS version number, cipher id).
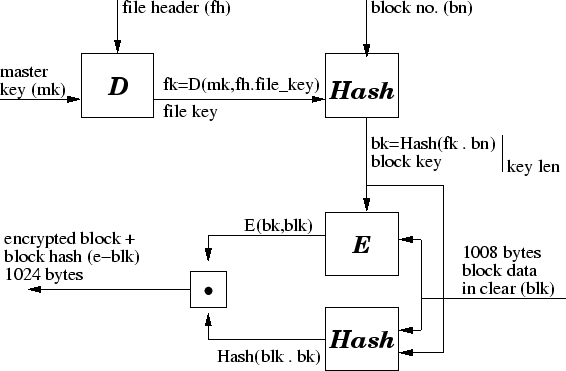
Each user 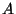 is associated with a master key
is associated with a master key 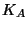 as
described in Section 4.
For each file
as
described in Section 4.
For each file 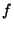 a file key
a file key 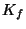 is randomly chosen.
The file key is encrypted using the master key
of the user and stored in the file-key field of the header.
Each block of a TCFS file consists of two parts: the data and the
authentication tag.
Each block of an encrypted TCFS file
is encrypted with the encryption algorithm
is randomly chosen.
The file key is encrypted using the master key
of the user and stored in the file-key field of the header.
Each block of a TCFS file consists of two parts: the data and the
authentication tag.
Each block of an encrypted TCFS file
is encrypted with the encryption algorithm 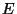 in CBC mode using
a different block key. Block
of unencrypted TCFS file are stored in clear.
The block key is computed by applying the hash function
to the concatenation of the file key and the block number.
The authentication tag of an authenticated TCFS file is computed
by hashing the concatenation of the block data and the block key.
On the other hand, unauthenticated TCFS files have an authentication tag
consisting of NULL bytes.
in CBC mode using
a different block key. Block
of unencrypted TCFS file are stored in clear.
The block key is computed by applying the hash function
to the concatenation of the file key and the block number.
The authentication tag of an authenticated TCFS file is computed
by hashing the concatenation of the block data and the block key.
On the other hand, unauthenticated TCFS files have an authentication tag
consisting of NULL bytes.
This way of encrypting and hashing the blocks exhibits
the following security characteristics:
- If a robust encryption scheme is used then
encrypted files cannot be read without knowledge of the file-key
or of the user master key.
- Since each file is encrypted using a different file-key,
it is not possible to check whether two encrypted files correspond
to the same cleartext.
- Moreover, since each block is encrypted using a different
block key, it is not possible to check whether two blocks of the
same file correspond to the same cleartext.
- The authentication tag is to prevent that data on the server is
modified. Obviously, since TCFS servers have physical access to the
filesystem there is nothing that could prevent the server from
modifying files. Our goal is thus to guarantee the user that
no modification will go unnoticed.
Our authentication mechanism guarantees:
- Modification of a block without recomputing
its authentication tag is easily detected by the TCFS client.
However, recomputing the authentication tag of a block requires
knowledge of the block key which in turn depends on the file
key which is encrypted using the user master key.
- Since each block authentication tag also depends by the block
offset without knowledge of the block key it is not possible
to insert foreign blocks of data or to swap two blocks of
the same files.
Moreover, since the authentication tag depends also on the file key,
it is not possible to import block from other files.
Figure 3:
Encryption of blocks in TCFS
 |


Next: Implementations
Up: The Design and Implementation
Previous: The Kerberized Key Management
The TCFS Team
2001-04-27

![]() is associated with a master key
is associated with a master key ![]() as
described in Section 4.
For each file
as
described in Section 4.
For each file ![]() a file key
a file key ![]() is randomly chosen.
The file key is encrypted using the master key
of the user and stored in the file-key field of the header.
Each block of a TCFS file consists of two parts: the data and the
authentication tag.
Each block of an encrypted TCFS file
is encrypted with the encryption algorithm
is randomly chosen.
The file key is encrypted using the master key
of the user and stored in the file-key field of the header.
Each block of a TCFS file consists of two parts: the data and the
authentication tag.
Each block of an encrypted TCFS file
is encrypted with the encryption algorithm ![]() in CBC mode using
a different block key. Block
of unencrypted TCFS file are stored in clear.
The block key is computed by applying the hash function
to the concatenation of the file key and the block number.
The authentication tag of an authenticated TCFS file is computed
by hashing the concatenation of the block data and the block key.
On the other hand, unauthenticated TCFS files have an authentication tag
consisting of NULL bytes.
in CBC mode using
a different block key. Block
of unencrypted TCFS file are stored in clear.
The block key is computed by applying the hash function
to the concatenation of the file key and the block number.
The authentication tag of an authenticated TCFS file is computed
by hashing the concatenation of the block data and the block key.
On the other hand, unauthenticated TCFS files have an authentication tag
consisting of NULL bytes.