
- 1
-
The open directory project.
See https://www.news.com/2100-1023-877568.html.
- 2
-
Safe Browsing API, June 2007.
See https://code.google.com/apis/safebrowsing/.
- 3
-
Safe Browsing diagnostic page, May 2008.
See
https://www.google.com/safebrowsing/diagnostic?site=yoursite.com.
- 4
-
ANAGNOSTAKIS, K. G., SIDIROGLOU, S., AKRITIDIS, P., XINIDIS, K., MARKATOS,
E., AND KEROMYTIS, A. D.
Detecting Targeted Attacks Using Shadow Honeypots.
- 5
-
ANDERSON, D. S., FLEIZACH, C., SAVAGE, S., AND VOELKER, G. M.
Spamscatter: Characterizing Internet Scam Hosting Infrastructure.
In Proceedings of the USENIX Security Symposium (August
2007).
- 6
-
BARFORD, P., AND YAGNESWARAN, V.
An Inside Look at Botnets.
Advances in Information Security. Springer, 2007.
- 7
-
BEM, J., HARIK, G., LEVENBERG, J., SHAZEER, N., AND TONG, S.
Large scale machine learning and methods.
US Patent: 7222127.
- 8
-
COOKE, E., JAHANIAN, F., AND MCPHERSON, D.
The Zombie Roundup: Understanding, Detecting, and Disturbing
Botnets.
In Proceedings of the first Workshop on Steps to Reducing
Unwanted Traffic on the Internet (July 2005).
- 9
-
DEAN, J., AND GHEMAWAT, S.
Mapreduce: Simplified data processing on large clusters.
In Proceedings of the Sixth Symposium on Operating System Design
and Implementation (Dec 2004), pp. 137-150.
- 10
-
EGELE, M., KRUEGEL, C., KIRDA, E., YIN, H., AND SONG, D.
Dynamic Spyware Analysis.
In Proceedings of the USENIX Annual Technical Conference
(June 2007).
- 11
-
FRANKLIN, J., PAXSON, V., PERRIG, A., AND SAVAGE, S.
An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Internet
Miscreants.
In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer and
Communications Security (CCS) (October 2007).
- 12
-
GU, G., PORRAS, P., YEGNESWARAN, V., FONG, M., AND LEE, W.
BotHunter: Detecting Malware Infection through IDS-driven Dialog
Correlation.
In Proceedings of the 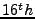 USENIX Security Symposium
(2007), pp. 167-182.
USENIX Security Symposium
(2007), pp. 167-182.
- 13
-
MODADUGU, N.
Web Server Software and Malware, June 2007.
See
https://googleonlinesecurity.blogspot.com/2007/06/web-server-software-and-malware.html.
- 14
-
MOORE, D., VOELKER, G. M., AND SAVAGE, S.
Inferring Internet Denial of Service Activity.
In Proceedings of 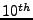 USENIX Security Symposium (Aug.
2001).
USENIX Security Symposium (Aug.
2001).
- 15
-
MOSER, A., KRUEGEL, C., AND KIRDA, E.
Exploring Multiple Execution Paths for Malware Analysis.
In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Symposium on Security and
Privacy (May 2007).
- 16
-
MOSHCHUK, A., BRAGIN, T., DEVILLE, D., GRIBBLE, S., AND LEVY, H.
SpyProxy: Execution-based Detection of Malicious Web Content.
- 17
-
MOSHCHUK, A., BRAGIN, T., GRIBBLE, S., AND LEVY, H.
A crawler-based study of spyware in the web.
In Proceedings of Network and Distributed Systems Security
Symposium (2006).
- 18
-
POLYCHRONAKIS, M., MAVROMMATIS, P., AND PROVOS, N.
Ghost Turns Zombie: Exploring the Life Cycle of Web-based Malware.
In Proceedings of the 1st USENIX Workshop on Large-Scale
Exploits and Emergent Threats (LEET) (April 2008).
- 19
-
PROJECT, H., AND ALLIANCE, R.
Know your enemy: Tracking Botnets, March 2005.
See https://www.honeynet.org/papers/bots/.
- 20
-
PROVOS, N., MCNAMEE, D., MAVROMMATIS, P., WANG, K., AND MODADUGU, N.
The Ghost in the Browser: Analysis of Web-based Malware.
In Proceedings of the first USENIX workshop on hot topics in
Botnets (HotBots'07). (April 2007).
- 21
-
RAJAB, M. A., ZARFOSS, J., MONROSE, F., AND TERZIS, A.
A Multifaceted Approach to Understanding the Botnet Phenomenon.
In Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM/USENIX Internet Measurement
Conference (IMC) (Oct., 2006), pp. 41-52.
- 22
-
RAMACHANDRAN, A., FEAMSTER, N., AND DAGON, D.
Revealing Botnet Membership using DNSBL Counter-Intelligence.
In Proceedings of the 2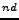 Workshop on Steps to Reducing
Unwanted Traffic on the Internet (SRUTI) (July 2006).
Workshop on Steps to Reducing
Unwanted Traffic on the Internet (SRUTI) (July 2006).
- 23
-
The Route Views Project.
https://www.antc.uoregon.edu/route-views/.
- 24
-
SEIFERT, C., STEENSON, R., HOLZ, T., BING, Y., AND DAVIS, M. A.
Know Your Enemy: Malicious Web Servers.
https://www.honeynet.org/papers/mws/, August 2007.
- 25
-
WANG, Y.-M., BECK, D., JIANG, X., ROUSSEV, R., VERBOWSKI, C., CHEN, S.,
AND KING, S.
Automated web patrol with strider honeymonkeys.
In Proceedings of Network and Distributed Systems Security
Symposium (2006), pp. 35-49.
- 26
-
WANG, Y.-M., NIU, Y., CHEN, H., BECK, D., JIANG, X., ROUSSEV, R.,
VERBOWSKI, C., CHEN, S., AND KING, S.
Strider honeymonkeys: Active, client-side honeypots for finding
malicious websites.
See https://research.microsoft.com/users/shuochen/HM.PDF.
- 27
-
YIN, H., SONG, D., EGELE, M., KRUEGEL, C., AND KIRDA, E.
Panorama: Capturing System-wide Information Flow for Malware
Detection and Analysis.
In Proceedings of the 14th ACM Conference of Computer and
Communication Security (October 2007).
Niels Provos
2008-05-13
