



Next: Combining Multiple Techniques using
Up: Detecting and Countering System
Previous: Sequence-based Techniques
To evaluate the intrusion detection wrappers with respect to their ability
to detect attacks, we tested the ID wrappers with several existing attacks.
These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in security-critical programs that
possess privileges to obtain a shell running as root.
We describe the programs and the attacks below.
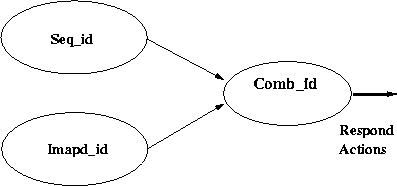
Figure 4:
Composing Two ID techniques
 |
- imapd
- Some versions of the Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP) server
contain a number of buffer-overflow bugs that allow a remote user to obtain
a shell running as root (CERT Advisory CA-97.09). We obtained an exploitation
script to
one of the bugs from RootShell (www.rootshell.com). The exploit script
carefully crafts the input to imapd that exceeds the size of a
special stack buffer and presents the name to the IMAP server to overwrite the saved
instruction pointer and execute the planted machine code.
The code then executes a shell running with root. We wrapped imapd
using a specification-based ID wrapper Imapd_id specific to
imapd and a sequence-based ID wrapper separately. Both wrappers were
able to detect the exploit script's attack.
- lpr
- Due to insufficient bounds checking on arguments which are
supplied by users, it is possible to overwrite the internal stack
space of some versions of the lpr program while it is executing.
This can allow an intruder to cause lpr to execute arbitrary
commands by supplying a carefully designed argument
to lpr (AUSCERT Advisory AA-96.12). These commands
will be run with the privileges of the lpr program. When lpr is setuid
root it may allow intruders to run arbitrary commands with root privileges.
We simulated the attack using a script from RootShell.
We wrapped lpr using a specification-based wrapper tailored for
lpr and the wrapper was able to detect the attack.
- lprm
- The program lprm is part of the printing subsystem. The program is
used to remove a job in the printer queue. There is a buffer-overflow
vulnerability in some versions of this program that allows a local user
to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges. We obtained a script
from Security Bugware (https://161.53.42.3/crv/security/bugs/list.html) and
tested a specification-based wrapper written for lprm with the script.
The specification-based wrapper detected the attack when lprm was
tricked to execute the Bourne shell.
- binmail
- The binmail program is the back-end mailer that delivers mail messages
to users' mailboxes. It does so by appending the messages to the mailbox
files directly. In some old versions, binmail changes the ownership
of a user's mailbox (usually /var/spool/mail/<username>)
back to the user after it appends a message if the mailbox file is not owned
by the user initially.
In particular, the binmail program (/bin/mail)
in 4.2 BSD Unix fails to reset the setuid bit of the mailbox file
after it appends a message and changes the owner of the file [5].
An attacker, who creates a mailbox file with the setuid bit on for the
superuser, can trick binmail into making the file to be setuid root
by invoking binmail to send a mail message to root.
We deployed the Mailstat wrapper and tested the wrapper with
an exploitation script we created. The wrapper detected the intrusion
immediately.



Next: Combining Multiple Techniques using
Up: Detecting and Countering System
Previous: Sequence-based Techniques
Calvin Ko
2000-06-13

