1
Introduction
Farsite [1] is a serverless, distributed file system that
logically functions as a centralized file server but is physically distributed
among a network of desktop workstations. Farsite provides the
location-transparent file access and reliable data storage commonly provided by
a central file server, without a central file server’s infrastructure costs,
susceptibility to geographically localized faults, and reliance on the
error-freedom and trustworthiness of system administrators.
Farsite replaces the physical security of a locked room with
the virtual security of cryptography and Byzantine-fault tolerance (BFT) [7]. It replaces high-reliability server hardware with
distributed redundant storage, computation, and communication provided by the
unused resources of existing desktop machines. And it replaces central system
administrators with autonomic processes that transparently migrate replicas of
file content and file-system metadata to adapt to variations in applied load,
changes in machines’ availability, and the arrival and departure of machines.
In 2002, we published a paper [1] describing a Farsite system that provides a Windows
file-system interface via a file-system driver, that stores encrypted replicas
of file content on remote machines, that autonomically rearranges these
replicas to maintain file availability [11], that provides transparent access to remotely stored
file content, that caches content on clients for efficiency, and that lazily propagates
file updates to remote replicas. This implementation also includes a directory
service that manages file-system metadata, issues leases to clients, and
receives metadata updates from clients. The directory service tolerates
malicious clients by validating metadata updates before applying them to the
persistent metadata state. In addition, the directory service tolerates
failures or malice in the machines on which it runs, by replicating its
execution on a BFT group of machines [7].
However, because every machine in a BFT group redundantly
executes the directory-service code, the group has no more throughput than a
single machine does, irrespective of the group size. Since this directory
service runs on a single BFT group, the rate at which the group can process
file-system metadata governs the maximum scale of the system. By contrast,
every other Farsite subsystem avoids scalability limitations either by implicit
parallelism or by relaxed consistency that is tolerable because it is concealed
by the directory service.
This paper presents a new design, implementation, and
evaluation of a directory service that is scalable and seamlessly distributed.
This work involves several novel techniques for partitioning file-system
metadata, maintaining name-space consistency, coordinating multi-machine
operations, and mitigating metadata hotspots. Experiments in a modest-sized
configuration show that our techniques enable the system to sustain throughput
that is proportional to system scale.
Our contributions include the following techniques:
·
tree-structured file identifiers
·
multi-machine operation protocol
·
recursive path leases
·
file-field leases
·
disjunctive leases
Our contributions also include the
end result, namely:
·
a file system that seamlessly distributes and
dynamically repartitions metadata among multiple machines
Section 2 overviews the Farsite system. Section 3 describes
the design decisions that drove the techniques detailed in Section 4 on
metadata partitioning and Section 5 on hotspot mitigation. Section 6 reports on
design lessons we learned, and Section 7 describes our implementation. Section
8 experimentally evaluates the system. Sections 9 and 10 describe future work
and related work. Section 11 summarizes and concludes.
2
Farsite overview
This section briefly summarizes the
goals, assumptions, and basic system design of Farsite. Many more details can
be found in our 2002 paper [1].
2.1
Goals
Farsite is Windows-based file system
intended to replace the central file servers in a large corporation or
university, which can serve as many as ~105 desktop clients [4]. Of Farsite’s many design goals, the key goal for the
present work is minimizing human system administration, which is not only a
significant cost for large server systems but also a major cause of system
failure [26]. In this paper, we address the specific sub-goal of automated load balancing.
2.2
Assumptions
Farsite is intended for wired
campus-area networks, wherein all machines can communicate with each other
within a small number of milliseconds, and network topology can be mostly
ignored. Farsite expects that machines may fail and that network connections
may be flaky, but it is not designed to gracefully handle long-term
disconnections.
Farsite’s intended
workload is that of normal desktop systems, which exhibit high access
locality, a low rate of updates that survive subsequent overwrites, and
infrequent, small-scale read/write sharing [20, 41]. It is not intended for high-performance parallel
I/O.
2.3
Basic system design
This section briefly overviews the
aspects of the Farsite system relevant to the metadata service, completely
ignoring issues relating to file content.
Each machine functions in two roles, a client that performs operations for its local user and a server that provides directory service
to clients. To perform an operation, a client obtains a copy of the relevant
metadata from the server, along with a lease [15] over the metadata. For the duration of the lease,
the client has an authoritative value for the metadata. If the lease is a write
lease, then the server temporarily gives up authority over the metadata,
because the lease permits the client to modify the metadata.
After the client performs the metadata operation, it lazily
propagates its metadata updates to the server. To make it easier for servers to
validate a client’s updates, the updates are described as operations rather
than as deltas to metadata state.
When the load on a server becomes excessive, the server
selects another machine in the system and delegates
a portion of its metadata to this machine.
From the perspective of the directory service, there is
little distinction between directories and data files, other than directories
have no content and data files may not have children. For simplicity, we refer
to them both as “files” except when clarity dictates otherwise.
3
Directory service design decisions
This section motivates our design
decisions and describes why we did not follow through with many of the design
ideas enumerated in our 2002 paper.
3.1
Fully functional rename
A fundamental decision was to support a fully functional rename
operation. Decades of experience by Unix and Windows users have shown that
fully functional rename is part of what makes a hierarchical file system a
valuable tool for organizing data. In fact, rename is the only operation that
makes non-trivial use of the name space’s hierarchy, by atomically changing the
paths of every file in a subtree while preserving open handles. Without rename,
the file-system structure is only slightly more involved than a flat name space
wherein the path separator (‘/’ in Unix, ‘\’ in Windows) is just another
character. It is slightly more involved because, for example, one can create a
file only if its parent exists, so in the flattened name space, one could
create a new name only if a constrained prefix of the name already exists.
Some prior distributed file systems have divided the name
space into user-visible partitions and disallowed renames across partitions;
examples include volumes in AFS [19], shares in Dfs [25], and domains in Sprite [27]. Anecdotal evidence suggests this is quite tolerable
as long as the system administrator exercises care when selecting files for each
partition: “[T]hey need to be closely
related, in order for rename to be useful, and there should be enough of them
so that the restriction on rename is not perceived by users as a problem [34].” However, in keeping with our goal of minimizing
system administration, we shied away from user-visible partitions, which demand
such careful organization [6]. Instead, we designed our metadata service to
present a semantically seamless name space.
3.2
Name-space consistency
Given a fully functional rename
operation, name-space consistency is necessary to avoid permanently
disconnecting parts of the file system, as a simplified example illustrates.
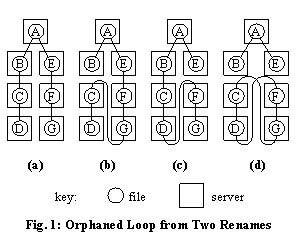
Fig. 1a shows a file-system tree in which every file is managed by a different
server. Client X renames file C to be
a child of file G, as shown in Fig. 1b, and Client Y independently renames file F to be a child of file D, as shown in
Fig. 1c. No single server is directly involved in both rename operations, and
each independent rename is legal. Yet, if both renames were allowed to proceed,
the result would be an orphaned loop, as shown in Fig. 1d.
Once we had a mechanism for scalable name-space consistency,
it seemed reasonable to use this mechanism to provide a consistent name space
for all path-based operations, not merely for renames.

3.3
Long-term client disconnection
Although Farsite is not intended to
gracefully support long-term client disconnections, we still need to decide
what to do when such disconnections occur. Since we employ a lease-based
framework, we attach expiration times – typically a few hours – to all leases
issued by servers. When a lease expires, the server reclaims its authority over
the leased metadata.
If a client had performed operations under the authority of
this lease, these operations are effectively undone when the lease expires.
Farsite thus permits lease expiration to cause metadata loss, not merely file
content loss as in previous distributed file systems. However, these situations
are not as radically different as they may first appear, because the
user-visible semantics depend on how applications use files.
For example, Microsoft's email program Outlook [28] stores all of its data, including application-level
metadata, in a single file. By contrast, maildir [40] uses the file system’s name space to maintain email
folder metadata. Under Outlook, content-lease expiration can cause email folder
metadata updates to get lost; whereas under maildir, expiring a file-system
metadata lease can cause the same behavior.
3.4
Prior design ideas
Our 2002 paper [1] envisioned a distributed directory service, for
which it presented several ideas that seemed reasonable in abstract, but which
proved problematic as we developed a detailed design.
Our intent had been
to partition file metadata among servers according to file path names. Each
client would maintain a cache of mappings from path names to their
managing servers, similar to a Sprite prefix table [43]. The client could verify the authority of the server
over the path name by evaluating a chain of delegation certificates extending
back to the root server. To diffuse metadata hotspots, servers would issue
stale snapshots instead of leases when the client load got too high, and
servers would lazily propagate the result of rename operations throughout the
name space.
Partitioning by path name complicates renames across
partitions, as detailed in the next section. In the absence of path-name
delegation, name-based prefix tables are inappropriate. Similarly, if
partitioning is not based on names, consistently resolving a path name requires
access to metadata from all files along a path, so delegation certificates are
unhelpful for scalability. Stale snapshots and lazy rename propagation allow
the name space to become inconsistent, which can cause orphaned loops, as
described above in Section 3.2. For these reasons, we abandoned these design
ideas.
4
Metadata partitioning
In building a distributed metadata
service, the most fundamental decision is how to partition the metadata among
servers. One approach is to partition by file path name, as in Sprite [27] and the precursor to AFS [32], wherein each server manages files in a designated
region of name space. However, this implies that when a file is renamed, either
the file’s metadata must migrate to the server that manages the destination
name, or authority over the destination name must be delegated to the server
that manages the file’s metadata. The former approach – migration without
delegation – is insufficient, because if a large subtree is being renamed, it may
be not be manageable by a single server. The latter approach may be plausible,
but coupling delegation to rename restricts the system’s ability to use
delegation for its primary purpose of load balancing. It also precludes clean
software layering, wherein a file’s semantic attributes, including its name,
are built on an abstraction that hides a file’s mobility.
The problems with partitioning by path name arise from a
name’s mutability. We avoid these problems by partitioning according to file
identifiers, which are not mutable. Our file identifiers have a tree structure,
which supports arbitrarily fine-grained partitioning (§ 4.1). This
partitioning is not user-visible, because operations can span multiple servers
(§ 4.2). Despite partitioning, the name space is kept consistent – in a
scalable fashion – by means of recursive path leases (§ 4.3).
4.1
Tree-structured file identifiers
Partitioning by file identifier is
not original to Farsite; it is also the approach taken by AFS [19] and xFS [2]. All three systems need to efficiently store
and retrieve information on which server manages each identifier. AFS addresses
this problem with volumes [34], and xFS addresses it with a similar unnamed
abstraction.
An AFS file identifier is the concatenation of two
components: The “volume identifier,”
which indicates the volume to which the file belongs, and the “file number,”
which uniquely identifies a file within the volume. All files in a volume
reside on the same server. Volumes can be dynamically
relocated among servers, but files cannot be dynamically repartitioned among
volumes without reassigning file identifiers. An xFS “file index number”
is similar; we defer more detailed discussion to Section 10 on related work.
4.1.2 File
identifier design issues
A main design goal for Farsite’s
file identifiers was to enable metadata repartitioning without reassigning file
identifiers. Specifically, we considered four issues:
- To maximize delegation-policy freedom, regions of
identifier space should be partitionable with arbitrary granularity.
- To permit growth, each server should manage an
unbounded region of file-identifier space.
- For efficiency, file identifiers should have a
compact representation.
- Also for efficiency, the (dynamic) mapping from file
identifiers to servers should be stored in a time- and space-efficient
structure.
4.1.3 Abstract
structure
Abstractly, a file identifier is a
sequence of positive integers, wherein the null sequence identifies the
file-system root. Each server manages identifiers beginning with a specified
prefix, except for those it has explicitly delegated away to other servers.
Fig. 2 shows a system of six servers, A
– F. The root server, A, manages all files except those whose
identifiers are prefixed by á1ñ, á3ñ, or á4ñ; server B
manages all files with identifiers prefixed by á1ñ but not by á1.3ñ; and
so forth. The file identifier space is thus a tree, and servers manage subtrees
of this space.
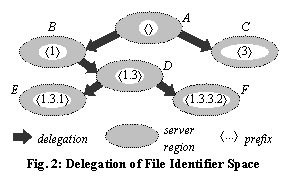
At any moment, some portion of each file identifier
determines which server manages the file; however, the size of this portion is
not fixed over time, unlike AFS file identifiers. For example, in the partitioning
of Fig. 2, a file with identifier á1.3.3.1ñ is managed by server D, because the longest delegated prefix of á1.3.3.1ñ is á1.3ñ. If
server D later delegates prefix á1.3.3ñ, the
file’s managing server will be determined by the first three integers in the
file identifier, namely á1.3.3ñ. This arbitrary partitioning granularity addresses
issue 1 above.
Because file identifiers have unbounded sequence length,
each server manages an infinite set of file identifiers. For example, server D can create a new file identifier by
appending any integer sequence to prefix á1.3ñ, as long as the resulting
identifier is not prefixed by á1.3.1ñ or á1.3.3.2ñ. This addresses issue 2.
4.1.4 Implementation
A file identifier’s integer sequence
is encoded into a bit string using a variant of Elias γ´ coding [13]. Because of the rule by which new file identifiers
are assigned (§ 4.1.5), the frequency distribution of integers within file
identifiers nearly matches the frequency distribution of files per directory.
We chose γ´ coding because it is optimally compact for the distribution we
measured in a large-scale study [9], thereby addressing issue 3.
Variable-length identifiers may be unusual, but they are not
complicated in practice. Our code includes a file-identifier class that stores
small identifiers in an immediate variable and spills large identifiers onto
the heap. Class encapsulation hides the length variability from all other parts
of the system.
To store information about which servers manage which
regions of file-identifier space, clients use a file map, which is similar to a Sprite prefix table [43], except it operates on prefixes of file identifiers
rather than of path names. The file map is stored in an index structure adapted
from Lampson et al.’s system for performing longest-matching-prefix search via
binary search [23]. With respect to the count of mapped prefixes, the
storage cost is linear, and the lookup time is logarithmic, thereby addressing
issue 4.
4.1.5 Creating
and renaming files
Each newly created file is assigned
an identifier formed from its parent’s identifier suffixed by an additional integer.
For example, in Fig. 3, the file named “y” under file á1.3ñ was created with
identifier á1.3.5ñ.
This rule tends to keep files that are close in the name space also close in
the identifier space, so partitioning the latter produces few cuts in the
former. This minimizes the work of path resolution, which is proportional to
the number of server regions along a path.
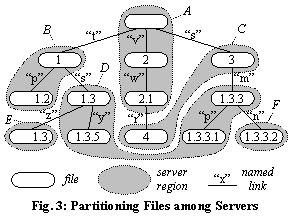
Renames can disrupt the alignment of the name and identifier
spaces. For example, Fig. 3 shows file á1.3.3ñ
having been renamed from its original name under file á1.3ñ to name “m” under file á3ñ.
Unless renames occur excessively, there will still be enough alignment to keep
the path-resolution process efficient.
4.2
Multi-server operations
The Windows rename operation
atomically updates metadata for three files: the source directory, the
destination directory, and the file being renamed. (Our protocol does not support
POSIX-style rename, which enables a fourth file to be overwritten by the
rename, although our protocol could possibly be extended to handle this case.)
These files may be managed by three separate servers, so the client must obtain
leases from all three servers before performing the rename. Before the client
returns its leases, thus transferring authority over the metadata back to the
managing servers, its metadata update must be validated by all three servers
with logical atomicity.
The servers achieve this atomicity with two-phase
locking: The server that manages the
destination directory acts as the leader,
and the other two servers act as followers.
Each follower validates its part of the rename, locks the relevant metadata fields, and notifies the leader. The
leader decides whether the update is valid and tells the followers to abort or
commit their updates, either of which unlocks the field. While a field is
locked, the server will not issue a lease on the field.
Since a follower that starts a multi-server operation is
obligated to commit if the leader commits, a follower cannot unlock a field on
its own, even to timeout a spurious update from a faulty client. Instead, the
leader centrally handles timeouts by setting a timer for each notification it
receives from a follower.
The followers must guarantee that the rename’s preconditions
still hold by the time the commit is received, which they can do because their
preconditions are local and therefore lockable. The leader, which manages the
destination server, can afford to check the one non-local condition, namely
that the file being moved is not an ancestor of the destination. This check is
facilitated by means of a path lease, as described in the following section.
4.3
Recursive path leases
As described in Section 3.2, servers
require a consistent view of the name space to ensure that a rename operation
does not produce an orphaned loop. More generally, Farsite provides name-space
consistency for all path-based operations. The naive way to do this is for the
servers managing all files along a path to issue individual leases on their
files’ children; however, this approach has poor scaling properties. In
particular, it makes the root server responsible for providing leases to all
interested parties in the system.
Our solution to this problem is the mechanism of recursive path leases. A file’s path lease is a
read-only lease on the chain of file identifiers of all files on the path from
the file-system root to the file. For example, a path lease on file á4ñ in
Fig. 3 would cover the chain {áñ, á2ñ, á2.1ñ, á4ñ}. Path leases are recursive, in that they are issued to
other files, specifically to the children of the file whose path is being
leased; a path lease on a file can be issued only when the file holds a path
lease from its parent. A path lease is accessible to the server that manages
the file holding the lease, and if the file is delegated to another server, its
path lease migrates with it. The recursive nature of path leases makes them
scalable; in particular, the root server need only deal with its immediate
child servers, not with every interested party in the system.
When a rename operation causes a server to change the
sequence of files along a path, the server must recall any relevant path leases
before making the change, which in turn recalls dependent path leases, and so
on down the entire subtree. The time to perform a rename thus correlates with
the size of the subtree whose root is being renamed. This implies that renames
near the root of a large file system may take considerable time to execute.
Such renames have considerable semantic impact, so this slowness appears
unavoidable.
5
Hotspot mitigation
No one, including us, has ever
deployed a file system with no user-visible partitions at our target scale of
~105 clients, so we do not know how such a system would be used in
practice. Nonetheless, to plausibly argue that our system can reach such a
scale, we believe it necessary to address the problem of workload hotspotting.
At the scales of existing deployments, file-system workloads
exhibit little sharing, and this sharing is mainly commutative, meaning that
the comparative ordering of two clients’ operations is not significant [3, 20]. However, even non-commutative sharing can result in
hotspotting if the metadata structure induces false sharing. We avoid false
sharing by means of file-field leases and disjunctive leases.
5.1
File-field leases
Rather than a single lease over all
metadata of a file, Farsite has a lease over each metadata field. The fields are each file attribute, a hash of the file
content, the file’s deletion disposition [16], a list of which clients have handles open, lists of
which clients have the file open for each of Windows’ access/locking modes [16], the file identifier of the file’s parent, and the
child file identifier corresponding to each child name. For the latter fields,
since there are infinitely many potential child names, we have a shorthand
representation of lease permission over all names other than an explicitly
excluded set; we call this the infinite
child lease.
File-field leases are beneficial when, for example, two
clients edit two separate files in the same directory using GNU Emacs [36], which repeatedly creates, deletes, and renames
files using a primary name and a backup name. Even though create and rename
operations modify the directory’s metadata, different filenames are used by
each client, so the clients access different metadata fields of the directory.
5.2
Disjunctive leases
For some fields, even a lease per
field can admit false sharing. In particular, this applies to the field
defining which clients have handles open and to the fields defining which
clients have the file open for each of Windows’ access/locking modes. Unlike
Unix’s advisory file locking, file locking in Windows is binding and integral
with open and close operations [16]. So, to process an open correctly, a client must
determine whether another client has the file open for a particular mode.
For example, if some client X has a file open for read access, no other client Y can open the file with a mode that
excludes others from reading. So, to know whether a “read-exclusive” open
operation should result in an error, client Y
requires read access to the file’s “read-mode” field to see if it contains any
client identifiers. If, at the same time, client Z opens the file for read access, it will require write access to
the read-mode field, which conflicts with client Y’s read access. This is a case of false sharing, because Y’s and Z’s opens are semantically commutative with each other.
In Farsite, this false sharing is avoided by applying disjunctive leases [12] to each the above fields. For a disjunctive leased
field, each client has a Boolean self
value that it can write and a Boolean other
value that it can read. The other value for each client x is defined as:
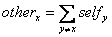
where the summation symbol indicates
a logical OR.
In the example above, when client X opens the file for read access, it sets its self value for the
read-mode field to TRUE, which causes
client Y’s other value to be TRUE, informing Y that some client has the file open for read access. When client Z opens the file for read access, it
sets its self value to TRUE, but this does
not change the other value that Y
sees.
Each client’s self value is protected by a write lease, and
its other value is protected by a read lease. The server manages these leases
to allow a client to access its values when this does not conflict with the
accesses of other clients. For example, if client X does not hold a self-write lease, it is not allowed to change its
self value; if this value is currently TRUE,
then the server can simultaneously grant other-read access to client Y and self-write access to client Z.
Disjunctive leases are beneficial for, for example, a
popular Microsoft Word [18] document. By default, Word attempts to open a file
for exclusive access, and if it fails, it then opens the file with shared
access. All clients after the first can read and write the appropriate
disjunctive mode bits without forcing the server to recall other clients’
leases.
6
Design lessons learned
This section enumerates some lessons
that we learned while designing Farsite’s distributed directory service.
A single field has a
single meaning. It might seem natural that if a client has a handle open
for write access on a file, the client has the ability to write the file’s
content. However, this does not follow. It is semantically permissible for two
clients to have write-access handles open concurrently, but it is not
logistically permissible for them to hold write leases on the file content
concurrently. At one point, we attempted to capture these separate meanings in
a single field to “simplify” the system, but this actually produced greater
complexity and subtlety.
Authority is rigorously
defined. In a distributed system wherein servers delegate authority to
other servers and lease authority to clients, it is crucial to define which
data is authoritative. When we were careless about this, it led to
circularities. For example, we once had a write lease that granted authority
over all unused names for a file’s children; however, whether a name is unused
is determined by the machine that has authority over the corresponding metadata
field, which is the client if and only if it holds a write lease. In our final
design, the lease that grants authority over all-but-a-few child names now
explicitly identifies the names it excludes, rather than implicitly excluding
names that are used.
The lease mechanism
is not overloaded with semantics. In one of our designs, if a client tried
to open a file that was already open for exclusive access by another client,
the server would refuse to issue the client a lease, which the client would
interpret as an indication of a mode conflict. Not only does this introduce a
special case into the lease logic, but it also obviates a key benefit of
leases: If the client repeatedly tries
to open the file, it will repeatedly ask the server for a lease, and the server
will repeatedly refuse until the file is closed by the other client. By
contrast, mode conflicts are now indicated by issuing the client an other-read
disjunctive lease (§ 5.2) on the incompatible mode. With this lease,
clients can locally determine whether the open operation should succeed.
Operations are performed
on clients and replayed on servers. This arrangement is common for
file-content writes in prior distributed file systems, and we found it just as
applicable to metadata updates. In an early design, we had considered
abandoning this strategy for multi-server rename operations, because we thought
it might be simpler for the servers to somehow perform the rename “on behalf
of” the client. In testing design alternatives, we found that the regular
approach was simpler even for multi-server rename, because it provides a simple
operational model: The client obtains
leases from all relevant servers, performs the operation locally in a single
logical step, and lazily sends the update to the servers. For multi-server operations,
the servers coordinate the validation of updates (§ 4.2).
Message recipients
need not draw inferences. In one of our design variants, when a client
released a lease, it did not indicate to the server whether it was releasing a
read lease or a write lease. Because these leases are mutually exclusive, the
server could infer which type of lease the client was releasing. However,
although this inference was always logically possible, it added some subtlety
in a few corner cases, which led to design bugs. The lease-release message now
explicitly identifies the lease, because we found that such changes vastly
simplify program logic with only a small additional expense in message length.
Leases do not
indicate values; they indicate knowledge of values. Before our design was
explicit about the fact that leases convey knowledge, we had a function called NameIsUsed that retuned TRUE when the client held a lease over a name
field with a non-null value. This led us to carelessly write !NameIsUsed(x) when we
really meant NameIsUnused(x).
It is easier to spot the error when the functions are named IKnowNameIsUsed and IKnowNameIsUnused. This is
even more important when the server validates a client’s update with logic such
as, “I know that the client knew that name X was unused.”
7
Implementation
7.1
Code structure
The directory-service code is split
into two main pieces: application logic and an atomic-action substrate. The
substrate provides an interface for executing blocks of application code with
logical atomicity, thus relegating all concerns about intra-machine race
conditions to an application-generic substrate of about 5K semicolon-lines in
C++.
We developed the application logic in the TLA+
system-specification language [22] and then translated it into about 25K
semicolon-lines of C++, nearly half of which is data-structure definitions and
support routines that were mechanically extracted from the TLA+ spec.
Within the application logic, all aspects of mobility are
handled in a bottom layer. Higher-layer
client code is written to obtain leases “from files” and to send updates “to
files,” not from and to servers.
The directory service does not currently employ Byzantine
fault tolerance, but the code is structured as a deterministic state machine,
so we expect integration with Farsite’s existing BFT substrate to be relatively
straightforward. As a consequence of the lack of BFT, a machine failure in the
current implementation can damage the name space, which is clearly not
acceptable for a real deployment.
7.2
Provisional policies
Our emphasis has been on mechanisms
that support a seamlessly distributed and dynamically partitioned file system.
We have not yet developed optimal policies for managing leases or determining
when servers should delegate metadata. For our experimental evaluation, we have
developed some provisional policies that appear to work reasonably well.
7.2.1 Lease-management
policies
Servers satisfy lease requests in
first-come/first-serve order. If a lease request arrives when no conflicting lease
is outstanding and no conflicting request is ahead in the queue, the request is
satisfied immediately.
For efficiency, a server might choose to promote a set of
child-field leases to an infinite child lease (§ 5.1). Our current policy
never does so; infinite child leases are issued only for operations that need
to know that the file has no children, namely delete and close.
The procedures for managing disjunctive leases (§ 5.2)
are fairly involved, as detailed in our tech report [12]. There are two cases that present policy freedom,
both of which allow the option of recalling self-write leases from some
clients, in the hope that a client’s self value is TRUE,
thereby coercing all remaining clients’ other values to TRUE. Our current policy never exercises this option. When
processing an other-read request, we recall all self-write leases, and when
processing a self-write request, we recall other-read leases.
7.2.2 Delegation
policy
A server considers a file to be active if the file’s metadata has been
accessed within a five-minute interval. The load on a region of file-identifier
space is the count of active files in the region. Machines periodically engage
in a pairwise exchange of load information, and a machine that finds its load
to be greater than twice the load on another machine will delegate to the
less-loaded machine.
To minimize fine-grained repartitioning, which can reduce
the efficiency of the file map (§ 4.1.4), our policy uses hysteresis to
avoid excessive rebalancing, and it transfers load in a few, heavily-loaded
subtrees rather than in many lightly-loaded subtrees.
8
Evaluation
We experimentally evaluate our
directory service in a system of 40 machines driven by microbenchmarks,
file-system traces, and a synthetic workload. We report on the effectiveness of
our techniques as well as the ability of those techniques to seamlessly
distribute and dynamically repartition metadata among servers.
8.1
Experimental configuration
We ran our experiments on 40
slightly out-of-date machines reclaimed from people’s desktops. Farsite
requires no distinction between client and server machines, but for clarity of
analysis, we designate half of the machines as clients and half as a pool for
servers; this allows us to vary their counts independently. The machines are a
mix of single- and dual-processor PIII’s with speeds ranging from 733 to 933
MHz and memory from 512 to 1024 MB.
Because Farsite’s servers are intended to run on random
people’s desktop machines, we do not want the server process to consume a
significant fraction of a machine’s resources. In a real deployment, we might
adaptively regulate the server process to keep it from interfering with the
user’s local processes [10]. For purposes of our experiments, we simulate the
limited usability of server machine resources by restricting each server’s rate
of disk I/O (Farsite’s bottleneck resource) to little more than what is needed
to support the metadata workload generated by a single client.
8.2
Workloads
We evaluate our system with six
workloads: a server snapshot, three microbenchmarks, a file-system trace from a
desktop machine, and a synthetic workload that mimics a set of eight user
tasks.
8.2.1 Departmental
server snapshot
Our simplest workload copies the
metadata of a departmental file server into Farsite. The file server contains
2.3M data files and 168K directories.
8.2.2 Conflicting
renames
This microbenchmark performs a
repeating sequence of four renames issued by two clients, as illustrated in
Fig. 1. Client X attempts to
transform Fig. 1a into Fig. 1b and back again, while client Y attempts to transform Fig. 1a into
Fig. 1c and back again.
8.2.3 Common-directory
editing
This microbenchmark has two clients
edit two separate files in the same directory. Each client’s operations follow
the pattern of GNU Emacs [36], as mentioned in Section 5.1. Each save in the
editor results in a creation, a deletion, and a rename, all of which modify
child fields in the directory’s metadata.
8.2.4 Common-file
opening
This microbenchmark has a client
create a file using shared-read/exclusive-write access. Then, 12 clients each
repeatedly open and close the file, in the manner mentioned in Section 5.2:
Each open is first attempted with shared-read/exclusive-write access, and when
this fails, the open is repeated with shared-read access.
8.2.5 Desktop
file-system trace
To demonstrate a real client
workload, we use a one-hour trace of file-system activity. This particular hour
within this particular trace was selected because it exhibits the statistically
most-typical activity profile of 10am-to-5pm file-system usage among 100
developers’ desktop machines we instrumented at Microsoft.
We also drove the system with 15 desktop traces running on
15 clients concurrently. However, multiple traces from independent desktop
machines exhibit no sharing, so such an experiment demonstrates no more than a
single trace does.
8.2.6 Synthetic
workload
To demonstrate a workload with a
moderate rate of shared metadata access, we use a synthetic workload driver
that models file-system workload with gremlins,
each of which mimics a user task according to random distributions. Four of the
gremlins simulate tasks that exhibit no sharing: entering data into a database;
editing text files in GNU Emacs [36]; editing, compiling, and linking a code project; and
downloading, caching, and retrieving web pages. Each client runs an instance of
all four gremlins, with their control parameters set to make their collective
activity roughly match the rate and profile of the desktop file-system trace
described above.
To this mix, we add four additional types of gremlins that
coordinate among multiple clients: One
gremlin simulates shared document editing, with the active reader and/or writer
changing every ~3 minutes. Another gremlin simulates an email clique using a
maildir [40] file-system-based email system; each client begins a
session every ~15 minutes, reads all new email with ~15-second peruse times,
and sends ~2 new messages with ~2-minute composition times. A third gremlin
simulates an RCS [39] revision-control system; each client begins a
session every ~30 minutes, checks out (co),
edits ~5 files, and checks in (ci).
Lastly, a custodial gremlin, once per ~30 minutes, renames directories near the
root of the file-system tree, above where the other gremlins are working. All
indicated times and counts are means of random distributions.
We choose a 15-client/15-server configuration as a basis,
and we also vary the count of clients and servers. For each experiment with N clients, we instantiate one custodial
gremlin and N of each other gremlin.
We run the gremlin workload for 4 hours.
In the basis experiment, the 15 clients performed 390
operations/second in aggregate. This resulted in an aggregate rate of 3.6 lease
requests, 8.3 lease grants, and 0.8 batched updates per second.
8.3
Results
This section reports on the
effectiveness of our main techniques: tree-structured file identifiers,
multi-server operations, path leases, file-field leases, and disjunctive
leases. It also reports on the results of those techniques, namely the load
balancing, proportional scaling, and semantic correctness of our directory
service.
8.3.1 Tree-structured
file identifiers
To validate our hypothesis that
tree-structured file identifiers can compactly represent real directory-size
and directory-depth distributions, we drive the system with a server snapshot
(§ 8.2.1). New file identifiers are created according to Farsite’s rule
for keeping files that are close in the name space also close in the identifier
space (§ 4.1.5). As a control, we use simulation to evaluate the use of
conventional fixed-size identifiers to satisfy this same condition.
Specifically, our control uses non-oracle greedy assignment, which successively
halves sub-regions of the flat identifier space for each new subdirectory in a
directory, and it assigns file identifiers to files in a directory linearly
within the directory’s sub-region of identifier space. When the optimal
sub-region is filled up, new identifiers spill into ancestor regions.
In the experimental run, the mean identifier length is 52
bits, the maximum is 107 bits, and the 99th percentile is 80 bits. Because file
identifiers grow logarithmically with file-system size, a much larger file
system would produce only slightly larger identifiers.
We performed three control runs. With 32-bit file
identifiers, only 16% of the server’s files were assigned identifiers within
their designated sub-region, and only the first 62% were assigned identifiers
at all, because eventually there were no free identifiers on the path from the
parent identifier all the way to the root. When the file-identifier length is
increased to 48 bits, which is the same size as the immediate representation of
our tree-structured file identifiers, all files obtained identifiers; however,
46% of them spilled outside their designated sub-region. Even with 107-bit
identifiers, which is the maximum size tree-structured identifier needed for
this workload, 5% of files spilled outside their designated sub-region.
Moreover, any fixed-size identifier scheme has a spillage cliff that will
eventually be reached as the file system grows.
8.3.2 Multi-server
operations and path leases
To characterize the multi-server
rename protocol and its use of path leases, we drive the system with a
worst-case workload of conflicting renames (§ 8.2.2), wherein all six
relevant files are on different servers.
Over 400 rename operations, the run produced 2404 messages
relating to requesting, recalling, issuing, and releasing path leases. It also
produced 2400 inter-server messages related to the two-phase locking in our
multi-server move protocol. On average, there were 12 server-to-server messages
per rename operation in this extreme worst case.
8.3.3 File-field
leases
To validate our hypotheses that
file-field leases prevent an instance of false sharing, we drive the system
with a workload of common-directory editing (§ 8.2.3). As a control, we
replace file-field leases with a single lease per file.
After 100 editor saves, the control run issued 202 file
leases, whereas the experimental run issued 6 child-field leases. In the
control run, the count of leases is proportional to editor saves, but in the
experimental run, the count of leases is constant.
The synthetic workload (§ 8.2.6) also demonstrates the
benefit of file-filed leases. Of the 110k leases the servers issued, 59% did
not require recalling other leases but would have required recalls if the lease
conflicts had been computed per file. This actually understates the benefit,
because a client whose lease has been recalled is likely to want it back,
leading to an arbitrarily greater degree of lease ping-ponging.
8.3.4 Disjunctive
leases
To validate our hypotheses that
disjunctive leases prevent an instance of false sharing, we drive the system
with a workload of common-file opening (§ 8.2.4). As a control, we replace
each disjunctive lease with a single-writer/multiple-reader lease.
After 100 iterations per client, the control run issued 1237
mode-field leases and recalled 1203 of them, whereas the experimental run
issued 13 mode-field leases and recalled one. In the control run, the lease
count is proportional to client open attempts, but in the experimental run, the
lease count is merely proportional to the count of clients.
8.3.5 Load
balancing
To validate our hypothesis that
dynamic partitioning effectively balances metadata load, we look at the loads
on the 15 server machines in a basis run of the synthetic workload
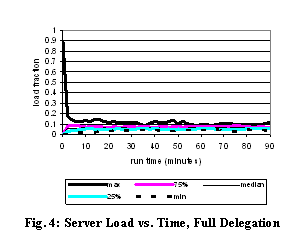
(§ 8.2.6). Fig. 4 shows the loads over the first 90 minutes of the 4-hour
run. Initially, the entire load is on the root server, but this is quickly
delegated away to other servers. If the load were perfectly balanced, each
server would handle 1/15th of the load, but the actual load on machines varies
from 3% to 14%, indicating that there is room for improvement in our delegation
policy.
As a control, we modify our delegation policy to delegate
each file at most once. This approximates an alternative system design that
attempts to balance load by statically assigning each file to a server when the
file is created. We could not implement this alternative directly, because
Farsite assumes that a file is created on the same server as its parent.
However, our control is a conservative approximation, because it can look at a
file’s activity for an arbitrary period after creation before deciding on an
appropriate server for the file. Fig. 5 shows the loads for the control, which
initially does a passable job of balancing the loads, but they become
progressively less balanced as time goes on.

8.3.6 Proportional
scaling
A key aspect of Farsite’s deployment
scenario is that every client can also be a server. To demonstrate that Farsite
is able to use a proportional server pool effectively, we ran the synthetic
workload (§ 8.2.6) in a suite of experiments with N clients and N server
machines, varying N from 1 to 20.
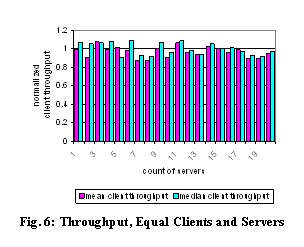
Fig. 6 illustrates the mean and median client throughput relative to the
15-client/15-server basis described above. The graph shows that per-client
throughput holds approximately constant as the system size varies; there is
some random variation, but it is not correlated to system scale. This
experiment shows that, at least at these modest scales, our mechanisms are
effective at preventing the root server (or any other resource) from becoming a
bottleneck that causes a decrease in throughput as scale increases.
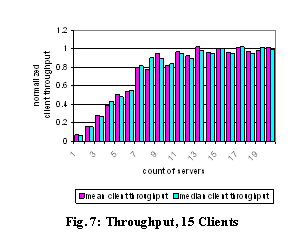
For contrast, we ran a suite of experiments with N server machines but a fixed load of 15
clients, as shown in Fig. 7. As long as the count of servers is not much below
the count of clients, the per-client throughput is not noticeably throttled by
available server resources. Because we throttle the servers’ I/O rates, smaller
server pools cause a drop in client throughput. This illustrates the need for
distributing the directory service in Farsite.
8.3.7 Semantic
correctness
Experiments with all of the
workloads demonstrate that our mechanisms successfully preserve file-system
semantics, even when the metadata is dynamically partitioned among servers. In
the file-system trace workload (§ 8.2.5), the results of the submitted
operations match the results when the trace is run on a local file system. The
microbenchmarks (§§ 8.2.2–4) and the gremlins (§ 8.2.6) know what the
results of their operations should be, and they verify that the system
functions correctly.
In the gremlin basis experiment, 8 operations spanned
multiple servers. Although this is a small fraction of the 2.1M operations performed,
even a single semantic failure is enough to annoy a real user. If Farsite’s
metadata partitioning were user-visible, these 8 operations could not have been
performed.
9
Future work
We see several areas for future work, including further analysis, additional
mechanism, improved policy, and completing integration with the rest of
Farsite.
9.1
Further analysis
Our synthetic workload (§ 8.2.6) exhibits a moderate degree of
shared metadata access, as indicated by measurements of distributed-file-system
usage [3]. It would be valuable to study the sensitivity of
the system to variations in the degree of sharing.
We would like to
study Farsite’s behavior at scales far larger than we could test in our lab.
Simulation may help to understand the behavior of our distributed algorithms at
the target scale of 105 machines.
9.2
Mitigating super-hotspots
If a very large number of clients
request concurrent, non-conflicting access to a particular metadata field, the
managing server may become overwhelmed by the load of issuing and recalling
leases. We envision diffusing this load with a blanket lease: a signed certificate that declares the field to have
a certain value guaranteed for a certain time, thus effectively granting every
client read access to the field. Whenever the count of lease requests exceeds a
threshold, a blanket lease is sent to all connected clients via a distribution
tree.
Because such leases cannot be recalled, if a client requests
a lease that conflicts with a blanket lease, the server must wait for the
blanket lease to expire before it can issue the conflicting lease. To prevent
the clients that had been using the blanket lease from hammering the server
with new lease requests, the server distributes a stifle certificate, which tells the clients not to make any
requests for the metadata until an indicated time, thus giving the server a
chance to satisfy the conflicting request and then issue a new blanket lease.
9.3
Improved delegation policy
Our current delegation policy
(§ 7.2.2) attempts to balance the distribution of load, under some basic
constraints to minimize fragmentation. There is much opportunity both to
improve efficiency and to reduce fine-grained repartitioning.
The delegation policy could also be extended to account for
variations in machine availability, similar to Farsite’s policy for
file-content placement [11].
9.4
Complete system integration
The directory service is not yet fully integrated with the rest of the
Farsite system. In particular, there is no bridge to the components that manage
file content. The main hurdle is modifying Farsite’s kernel-level file-system
driver to understand the leases used by the distributed directory service,
which differ considerably from those used by Farsite’s earlier centralized
directory service.
The directory service code is not currently built on top of
Farsite’s BFT substrate. However, we structured the code with BFT in mind, so
this integration should not be a significant challenge.
10
Related work
For comparison with our system, a convenient way to categorize
distributed file systems is by the method they use to partition metadata.
10.1 Dynamically
partitioning the name tree
Weil et al. [42] propose a file-system metadata service that
dynamically partitions metadata by subtrees of the name space. They evaluate
this proposal via simulation rather than by implementation and experimentation.
Despite their use of simulation, they only study configurations up to 50
machines, which is not much larger than our evaluation. They conclude that
subtree partitioning is more efficient than either hash-based metadata
partitioning or a hybrid of the two.
Although their proposed partitioning scheme bears similarity
to ours, a key difference is that our dynamic partitioning is based on
tree-structured file identifiers rather than the name-space tree, which we
argue (§ 4) poses significant challenges for rename operations. It is not
clear that Weil et al.’s simulations assess the cost of performing renames in
their proposed system.
10.2 Statically
partitioning the name tree
Several distributed file systems partition their metadata statically by
path name. Examples include NFS and the Automounter from Sun, CIFS and Dfs from
Microsoft, and Sprite.
NFS [31] and CIFS [17] both afford remote access to server-based file
systems, but neither one provides a global name space. A collection of NFS
“mountpoints” can be made to appear as a global name space when mounted
uniformly with the client-side Automounter [5]. A collection if CIFS “shares” can be assembled into
a global name space by the Dfs [25] client/server redirection system. NFS and CIFS both
require all client operations to be sent to the server for processing. The
Automounter and Dfs both operate on path names.
Sprite [27] partitions the file-system name space into
“domains.” Clients find the managing server for a domain initially by broadcast
and thereafter by use of a prefix table [43], which maps path names to servers according to longest-matching-prefix.
Farsite’s file map (§ 4.1.4) is similar to Sprite’s prefix table, except
that it operates on file identifiers rather than path names.
Mountpoints, shares,
and domains are all user-visible. It is not possible to perform rename operations
across them, unlike Farsite’s transparent partitions. Furthermore, none of
these systems provides support for automatic load balancing.
10.3 Partitioning
groups of file identifiers
AFS [19] partitions files using a hybrid scheme based partly
on file name and partly on file identifier. As in Sprite, the name space is
statically partitioned by path name into partial subtrees. Each subtree, known
as a “volume,” is dynamically assigned to a server. Files are partitioned among
volumes according to file identifier, which embeds a volume identifier. Like
Sprite’s shares, AFS volumes are user-visible with regard to rename.
xFS [2] partitions metadata by file identifier, which it
calls the “file index number.” A globally replicated manager map uses a portion of a file’s index number to determine
which machine manages the file’s metadata. All files whose index numbers
correspond to the same manager-map entry are managed by the same machine, so
they correspond closely to an AFS volume, although xFS presents no name for
this abstraction. Whereas AFS volumes provide name-space locality, xFS files
are partitioned according to which client originally created the file. Relocating
groups of files, which requires consistently modifying the global manager map,
is not implemented in the xFS prototype. xFS is intended to have no
user-visible partitions, but the paper includes no discussion of the rename
operation or of any name-space consistency mechanisms.
In both AFS and xFS,
fine-grained repartitioning of files requires changing files’ identifiers,
which entails significant administrator intervention.
10.4 Partitioning
by hashing file names
Another way to partition metadata is to use a distributed hash table.
CFS [8] and PAST [29] are scalable, distributed storage systems based,
respectively, on the Chord [37] and PASTRY [30] distributed hash tables. CFS and PAST provide only
flat name spaces, unlike the hierarchical name space provided by Farsite.
10.5 Partitioning
at the block level
A markedly different approach is commonly employed by cluster file
systems, which construct a distributed, block-level storage substrate for both
file content and metadata. The metadata is partitioned at the level of the
block-storage substrate. At the file-system level, all metadata is accessible
to all servers in the cluster, which use a distributed lock manager to
coordinate their metadata accesses.
A typical example is
the Global File System [35], which builds a “network storage pool” from a
diverse collection of network-attached storage devices. High-speed connectivity
between all servers and all storage devices is provided by a storage area
network (SAN). Servers do not communicate directly with each other; rather,
lock management of shared storage devices is provided by storage device
controllers.
Instead of running
over a SAN, the Frangipani [38] file system is built on the Petal [24] distributed virtual disk, which pools the storage
resources of multiple server machines into logically centralized disk.
High-speed connectivity is provided by a switched ATM network. Frangipani
servers use a message-based lock-management scheme, and they maintain
consistent configuration information using Paxos [21].
Because these
systems do not partition metadata, their performance can suffer due to
contention. IBM’s GPFS [33] introduces several techniques to decrease the
likelihood of contended metadata access. First, shared-write locks allow
concurrent updating of non-name-space-critical metadata. Specifically, updates
to file size and modification time are committed lazily. Second, the allocation
map is divided into large regions. A single allocation
manager server keeps the allocation map loosely up-to-date and directs
different servers to different regions of the map. Deletions are shipped to the
servers managing the relevant regions of the map. Third, distributed lock
management employs a token protocol. Although this is supervised by a central token manager, several optimizations
reduce the message load, including batching, prefetching, and hysteresis.
These systems all
require tight coupling via SAN or switched network, unlike Farsite, which runs
over a LAN. Because their metadata is partitioned at the level of opaque
blocks, lock contention can limit the scalability of some metadata operations [33 (Fig. 4)].
10.6 Not
partitioning
The Google File System [14] does not partition metadata at all. All metadata updates
are centralized on a single server. The metadata workload is kept low by
providing a limited operational interface for append-only or append-mostly
applications that can tolerate duplicated writes.
11
Summary and conclusions
We have developed a distributed
directory service for Farsite [1], a logically centralized file system physically
distributed among a wired network of desktop machines on the campus of a large
corporation or university. Farsite provides the benefits of a central file
server without the additional hardware cost, susceptibility to geographically
localized faults, and frequent reliance on system administrators entailed by a
central server.
Prior to this work, Farsite’s metadata service was centralized
on a single BFT group of machines, which could not scale to the normal
file-system metadata loads [41] of the ~105 desktop computers [4] in our target environment. In designing a
distributed replacement for this service, a key goal was to automate the
balancing of workload among servers, so as to minimize the need for human
system administration.
A significant concern was that as file metadata is
dynamically relocated among servers to balance load, users might observe
confusingly varying semantics over time. To avoid this situation, we designed
our directory service so that the partitioning of files among servers is not
user-visible. Specifically, Farsite supports a fully functional rename
operation, which allows renames to be performed anywhere in the name space,
unlike in previous distributed file systems [19, 25, 27]. Since a rename operation may thus span multiple
servers, the servers employ two-phase locking to coordinate their processing of
a rename.
The name space is strongly consistent. Although necessary
only for rename to prevent the accidental disconnection of parts of the
directory tree, strong consistency is maintained for all path-based operations.
To avoid the scalability limitation of having servers issue leases on their
files’ children to all interested parties, we employ recursive path leases,
which are successively issued from each file to its child files, and which
inform a file of its current path name.
We partition files among servers according to file
identifier, because the alternative of partitioning by file name is complicated
by the mutability of names under the rename operation. Our file identifiers
have a tree structure that stays approximately aligned with the tree structure
of the name space, so files can be efficiently partitioned with arbitrary
granularity while making few cuts in the name space.
To mitigate the hotspots that might arise in a deployed
system, our service has a separate lease over each metadata field of a file,
rather than a single lease over all metadata of a file. For certain fields
relating to Windows’ deletion semantics and access/locking modes [16], we break down fields even further by means of
disjunctive leases, wherein each client supplies an independent Boolean value
for its part of the field, and each client observes the logical OR of other clients’ values. With the exception
of disjunctive leases, all of our techniques are directly applicable to
non-Windows file systems.
Although our emphasis was on mechanisms, we also developed
some provisional policies to drive those mechanisms. For managing leases, we
used the simplest approaches we could: issuing leases on a first-come/
first-serve basis, promoting leases only when necessary, and pessimistically
recalling all potentially conflicting disjunctive leases. To relocate file
metadata, machines attempt to balance recent file activity, using a pairwise
exchange with hysteresis.
We experimentally evaluated our service in a system of 40
machines, using a server snapshot, microbenchmarks, traces, and a synthetic
workload. The snapshot shows that tree-structured file identifiers can compactly
represent a real file-server directory structure. Microbenchmarks show that
file-field leases and disjunctive leases mitigate hotspots by preventing
instances of false sharing. The trace and synthetic workloads show that dynamic
partitioning effectively balances metadata load. They also show that the system
workload capacity increases in proportion to the system size, which is a crucial property for achieving our
target scale of ~105 machines.
Acknowledgements
The authors deeply appreciate the long-running
support and encouragement this effort has received from the other members of
the Farsite team: Atul Adya, Bill Bolosky, Miguel Castro, Ronnie Chaiken, Jay
Lorch, and Marvin Theimer.
The effort of distilling our work into a presentable form
has been assisted by many people, beginning with Butler Lampson, who helped us
hone the paper’s focus. Early versions of the paper received valuable comments
from Rich Draves, John Dunagan, Jeremy Elson, Leslie Lamport, Marc Shapiro,
Marvin Theimer, Helen Wang, Lidong Zhou, and Brian Zill. The final version has
benefited greatly from the many detailed comments and suggestions made by the
anonymous OSDI reviewers and especially from the meticulous attention of our
shepherd, Garth Gibson.
We also extend our thanks to Robert Eberl of MSR Tech
Support for his help in collecting the departmental server snapshot described
in Section 8.2.1.
References
[1] A.
Adya, W. J. Bolosky, M. Castro, R. Chaiken, G. Cermak, J. R. Douceur, J.
Howell, J. R. Lorch, M. Theimer, R. P. Wattenhofer. “FARSITE: Federated,
Available, and Reliable Storage for an Incompletely Trusted Environment,” 5th OSDI, Dec 2002.
[2] T. Anderson, M. Dahlin, J. Neefe, D. Patterson, D. Roselli, R. Wang.
“Serverless Network File Systems,” 15th
SOSP, 1995.
[3] M.
G. Baker, J. H. Hartman, M. D. Kupfer, K. W. Shirriff, J. K. Ousterhout.
“Measurements of a Distributed File System,” 13th SOSP, 1991.
[4] W.
J. Bolosky, J. R. Douceur, D. Ely, and M. Theimer, “Feasibility of a Serverless
Distributed File System Deployed on an Existing Set of Desktop PCs,”
SIGMETRICS 2000, Jun 2000.
[5] B.
Callaghan, T. Lyon. “The Automounter,” Winter
USENIX Conf. 30 (3), 1989.
[6] A.
Campbell. Managing AFS: The Andrew File
System, Prentice Hall, 1998.
[7] M.
Castro and B. Liskov, “Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance,” 3rd OSDI,
Feb 1999.
[8] F.
Dabek, M. F. Kaashoek, D. Karger, R. Morris, I.
Stoica, “Wide-Area Cooperative Storage with CFS,” 18th SOSP, Oct 2001.
[9] J.
R. Douceur, W. J. Bolosky. “A Large-Scale Study of File-System Contents,” SIGMETRICS ’99, May 1999.
[10] J.
R. Douceur, W. J. Bolosky. “Progress-Based Regulation of Low-Importance
Processes,” 17th SOSP, Dec 1999.
[11] J.
R. Douceur, R. P. Wattenhofer, “Optimizing File Availability in a Secure
Serverless Distributed File System,” 20th
SRDS, Oct 2001.
[12] J.
R. Douceur, J. Howell. “Black Box Leases,” Microsoft
Research Tech Report MSR-TR-2005-120,
2005.
[13] P.
Elias. “Universal Codeword Sets and Representations of the Integers,” IEEE Trans. Info. Theory 21(2), 1975.
[14] S.
Ghemawat, H. Gobioff, S-T. Leung. “The Google File System,” 19th SOSP, 2003.
[15] C.
G. Gray, D. R. Cheriton. “Leases: An Efficient Fault-Tolerant Mechanism for
Distributed File Cache Consistency,” 12th
SOSP, 1989.
[16] J. M. Hart. Win32 System
Programming: A Windows(R) 2000 Application Developer's Guide, Second Edition,
Addison-Wesley, 2000.
[17] C. R. Hertel. Implementing
CIFS: The Common Internet File System, Prentice Hall, 2003.
[18] B. Heslop, D. Angell, P. Kent. Word
2003 Bible, Wiley, 2003.
[19] J. Howard, M. Kazar, S. Menees, D. Nichols, M. Satyanarayanan, R.
Sidebotham, M. West. “Scale and Performance in a Distributed File System,” TOCS 6(1), Feb 1988.
[20] J. Kistler, M. Satyanarayanan. “Disconnected
operation in the Coda File System,” TOCS
10(1), Feb 1992.
[21] L.
Lamport. “The Part-Time Parliament,” TOCS
16(2), 1998.
[22] L.
Lamport. Specifying Systems.
Addison-Wesley, 2003.
[23] B. W. Lampson, V. Srinivasan, G. Varghese. “IP Lookups using
Multiway and Multicolumn Search,” IEEE/ACM
Trans. Networking 7(3), 1999.
[24] E. Lee, C. Thekkath. “Petal: Distributed Virtual Disks,” 7th ASPLOS, 1996.
[25] T. Northrup. NT Network
Plumbing: Routers, Proxies, and Web Services, IDG Books, 1998.
[26] D. Oppenheimer, A. Ganapathi, D. A. Patterson. “Why Do Internet
Services Fail, and What Can Be Done About It?” 4th USITS, Mar 2003
[27] J. K. Ousterhout, A, R. Cherenson, F. Douglis, M. N. Nelson, B. B.
Welch. “The Sprite Network Operating System,” IEEE Computer Group Magazine 21 (2), 1988.
[28] T. Rizzo. Programming
Microsoft Outlook and Microsoft Exchange 2003, Third Edition, Microsoft
Press, 2003.
[29] A. Rowstron and P. Druschel. “Storage Management and Caching in
PAST, a Large-Scale, Persistent Peer-to-Peer Storage Utility”, 18th SOSP,
Oct 2001.
[30] A.
Rowstron, P. Druschel, “Pastry: Scalable, Distributed Object Location and Routing
for Large-Scale Peer-to-Peer Systems”, Middleware
2001, Nov 2001.
[31] R. Sandberg, D. Goldberg, S. Kleiman, D. Walsh, B. Lyon. “Design and
Implementation of the Sun Network File System,” USENIX 1985 Summer Conference, 1985.
[32] M. Satyanarayanan, J. H. Howard, D. A. Nichols, R. N. Sidebotham, A.
Z. Spector, M. J. West. "The ITC Distributed File System: Principles and
Design," 10th SOSP, Dec 1985.
[33] F. Schmuck, R. Haskin. “GPFS: A Shared-Disk File System for Large
Computing Clusters,” 1st FAST, 2002.
[34] B. Sidebotham. “Volumes: The Andrew File System Data Structuring
Primitive,” EUUG Conference Proceedings, Aug 1986.
[35] S. R. Soltis, G. M. Erickson, K. W. Preslan, M. T. O’Keefe, T. M.
Ruwart. “The Global File System: A File System for Shared Disk Storage,” 1997
http://www.diku.dk/undervisning/2003e/314/papers/
soltis97global.pdf
[36] R. M. Stallman. GNU Emacs
Manual, For Version 21, 15th Edition, Free Software Foundation, 2002.
[37] I.
Stoica, R. Morris, D. Karger, M. F. Kaashoek, H. Balakrishnan, “Chord: A
Scalable Peer-to-Peer Lookup Service for Internet Applications,” SIGCOMM 2001, Aug 2001.
[38] C. Thekkath, T. Mann, E. Lee. “Frangipani: A Scalable Distributed
File System,” 16th SOSP, Dec 1997.
[39] W. Tichy. “RCS: A System for Version Control,” Software–Practice & Experience 15(7), 1985.
[40] Sam Varshavchik. “Benchmarking mbox versus maildir,” 2003
http://www.courier-mta.org/mbox-vs-maildir/
[41] W. Vogels. “File System Usage in Windows NT 4.0,” 17th SOSP, Dec 1999.
[42] S. A. Weil, K. T. Pollack, S. A. Brandt, E. L. Miller. “Dynamic
Metadata Management for Petabyte-Scale File Systems,” Supercomputing 2004, 2004.
[43] B. Welch, J. Ousterhout. “Prefix Tables: A
Simple Mechanism for Locating Files in a Distributed System,” 6th ICDCS, 1986.

