 |

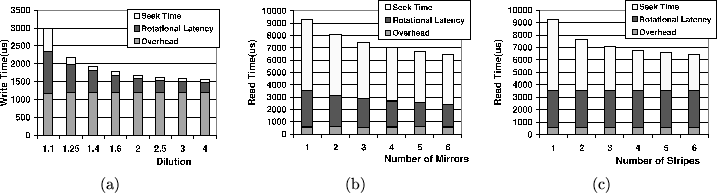
An EW-Array combines three techniques: eager-writing, mirroring, and striping. One commonality shared by all three of these techniques is that they all need extra disk capacity to be effective. We first examine individually how performance under each technique improves in response to increased capacity. We then analyze their combined effect. We use simple random workloads and simulation results in this section to study these techniques. More details about the simulation environment and results from more realistic workloads will be presented in later sections.
 |